Abstract
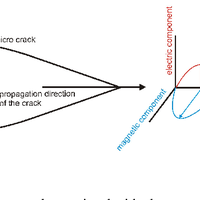
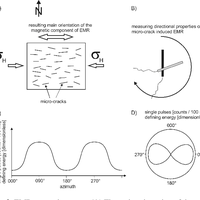
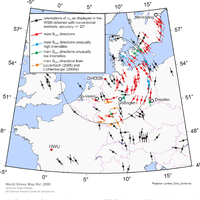
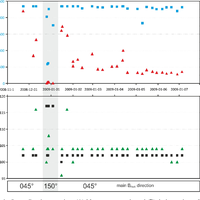
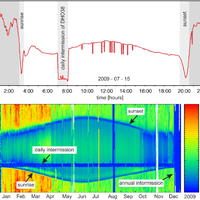
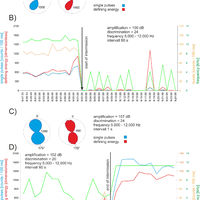
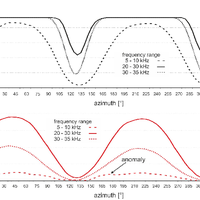
In recent years, the electromagnetic radiation (EMR) method has been used to detect faults and to determine main horizontal stress directions from variations in intensities and directional properties of electromagnetic emissions, which are assumed to be generated during microcracking. Based on a large data set taken from an area of about 250 000 km2 in Northern Germany, Denmark, and southern Sweden with repeated measurements at one location during a time span of about 1.5 yr, the method was systematically tested. Reproducible observations of temporary changes in the signal patterns, as well as a strongly concentric spatial pattern of the main directions of the magnetic component of the EMR point to very low frequency (VLF) transmitters as the main source and hence raise serious concerns about the applicability of the method to determine recent crustal stresses. We conclude that the EMR method, at its current stage of development, does not allow determination of the main horizontal stress directions. © Author(s) 2012. CC Attribution 3.0 License.
Figures
Register to see more suggestions
Mendeley helps you to discover research relevant for your work.
Cite
CITATION STYLE
Krumbholz, M., Bock, M., Burchardt, S., Kelka, U., & Vollbrecht, A. (2012). A critical discussion of the electromagnetic radiation (EMR) method to determine stress orientations within the crust. Solid Earth, 3(2), 401–414. https://doi.org/10.5194/se-3-401-2012