Abstract
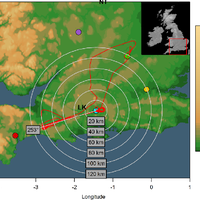
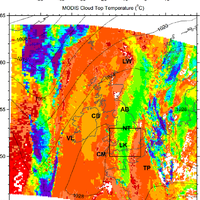
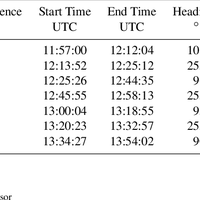
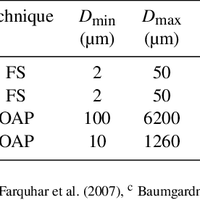
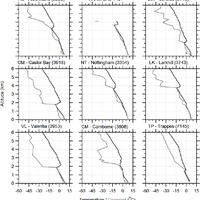
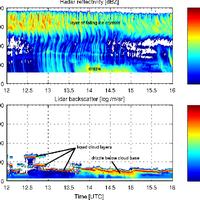
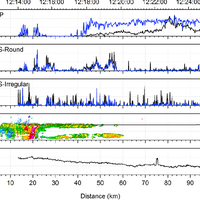
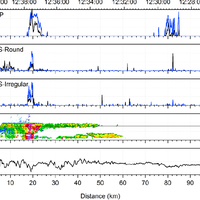
Simultaneous observations of cloud microphysical properties were obtained by in-situ aircraft measurements and ground based Radar/Lidar. Widespread mid-level stratus cloud was present below a temperature inversion (∼5 °C magnitude) at 3.6 km altitude. Localised convection (peak updraft 1.5 m s -1) was observed 20 km west of the Radar station. This was associated with convergence at 2.5 km altitude. The convection was unable to penetrate the inversion capping the mid-level stratus. The mid-level stratus cloud was vertically thin (∼400 m), horizontally extensive (covering 100 s of km) and persisted for more than 24 h. The cloud consisted of supercooled water droplets and small concentrations of large (∼1 mm) stellar/plate like ice which slowly precipitated out. This ice was nucleated at temperatures greater than -12.2 °C and less than -10.0 °C, (cloud top and cloud base temperatures, respectively). No ice seeding from above the cloud layer was observed. This ice was formed by primary nucleation, either through the entrainment of efficient ice nuclei from above/below cloud, or by the slow stochastic activation of immersion freezing ice nuclei contained within the supercooled drops. Above cloud top significant concentrations of sub-micron aerosol were observed and consisted of a mixture of sulphate and carbonaceous material, a potential source of ice nuclei. Particle number concentrations (in the size range 0.1
Figures
Register to see more suggestions
Mendeley helps you to discover research relevant for your work.
Cite
CITATION STYLE
Crosier, J., Bower, K. N., Choularton, T. W., Westbrook, C. D., Connolly, P. J., Cui, Z. Q., … Blyth, A. M. (2011). Observations of ice multiplication in a weakly convective cell embedded in supercooled mid-level stratus. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 11(1), 257–273. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-11-257-2011